
It was probably very nice to have both the moral and technical high ground in dealing with brutal but backward dictators. Deep Packet Inspection was initially developed for commercial use, but many authoritarian countries use it in their censorship and surveillance systems, including the Russian Sovereign Internet. Changing pictureįirst, it became increasingly evident that the TOR project enabled the Dark Web, populated with hackers, drug and gun dealers, and this picture was very far from the bright and shiny community of activists fighting dictators.Īnd second, the dictators found a way to block TOR, also using technology developed in democracies. Back then Russia's interior ministry offered 3.9 million rubles ($86,000) for research on cracking TOR, but was forced to cancel the project due to the lack of any breakthrough. Moscow challenged TOR unsuccessfully in 2014, two years after Internet censorship was introduced in the country. It all went well, and TOR seemed unbeatable for years, even in Russia. It was a scheme in which technically advanced democracies helped technically backward authoritarian regimes withstand repression by supplying technology to activists, not least to help them provide access to content produced by democracies.
#Blocking tor network free
Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights, and Labor, the International Broadcasting Bureau - which supports Voice of America and Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty - Internews and Human Rights Watch. The TOR project was supported financially by the U.S. In other words, TOR became the latest addition to the long tradition started by radio sets supplied by the British and Americans to the resistance in Nazi-occupied Europe, and copying machines smuggled beyond the Iron Curtain. From then on, the TOR Project, now a nonprofit, was largely seen as a technology developed and maintained by democratic countries to help activists in dictatorships bypass censorship in their countries.
#Blocking tor network code
military released the code for TOR, and the Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF) started to fund TOR developers to continue the project. spies a way to communicate with their assets securely using the Internet, and doing it by hiding their traffic in millions of other people’s traffic. Naval Research Laboratory to protect American intelligence communications online - essentially to give U.S. It was developed in the mid 1990s in the U.S. However, TOR was political from the beginning. VPNs, or virtual private networks, were developed when companies understood they needed a secure way to share data between different offices, and to allow employees to access sensitive files remotely and safely. Many technologies the users use today to avoid censorship were developed as commercial tools. But the significance of this development is much bigger.
#Blocking tor network software
TOR was Russia’s next natural target because the software allows users to access websites and pages blocked by the authorities. Apple has already been forced to turn it off in China, Belarus, Colombia, Egypt, Kazakhstan, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Turkmenistan, Uganda and the Philippines, citing ‘regulatory requirements’ in those countries. Private Relay was designed to encrypt all the traffic leaving the user’s device so no one can intercept it. And then Apple turned off its Private Relay service in Russia. In September, eight more popular VPNs were blocked. In the summer, Roskomnadzor blocked the first two VPNs, then the popular browser Opera killed support for its VPN.
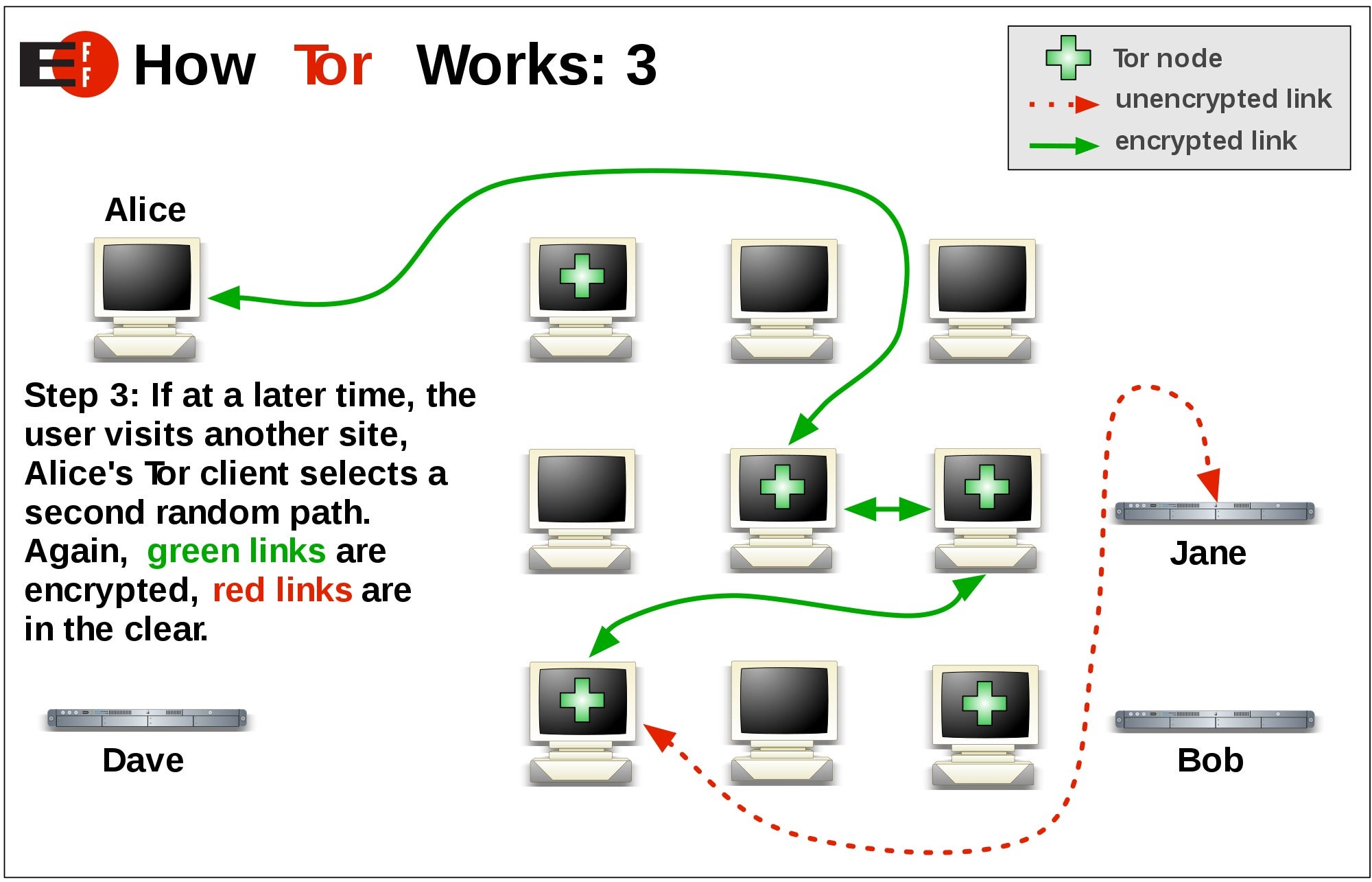
Throughout 2021, Russia’s Internet censors mounted a systematic attack on technologies that could be used by the country’s users to bypass censorship.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
